02 - SSA - Physical Science Review (6.P.13.1 / 13.3)
Quiz by Oksana Tariche
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measure skillsfrom any curriculum
Measure skills
from any curriculum
Tag the questions with any skills you have. Your dashboard will track each student's mastery of each skill.
With a free account, teachers can
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
21 questions
Show answers
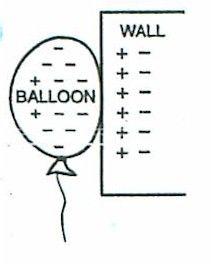
- Q1Luis rubbed a balloon on his hair and held the balloon next to the wall. He observed the balloon stick to the wall. Which of the following is responsible for the balloon sticking to the wall?FrictionMagnetic forceGravityElectric force30s
- Q2Gravity is a force that every mass exerts on every other mass. When you jump up in the air, not only does the Earth exert a gravitational force on you, but you also exert a gravitational force on the Earth. You, of course, fall back down to the Earth. Which of the following explains why the Earth is not moving toward you when you jump up in the air?Earth's fixed orbit around the Sun keeps it from moving.You don't weigh enough to affect Earth's surface.Your mass is very small compared to Earth's mass.Earth exerts a gravitational force on itself.30s
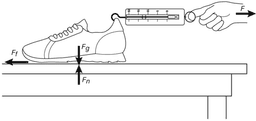
- Q3Meg designs an experiment to see which of three types of sneakers provides the most friction. She uses the equipment listed below. 1. Sneaker 1 3. Sneaker 3 2. Sneaker 2 4. Spring scale She uses the setup illustrated above and pulls the spring scale to the left. In what direction does the force of friction act?To the rightDownwardUpwardTo the left30s
- Q4Penny says that dust particles in space cannot be pulled together by gravity because they have very little mass. Emma says as long as the dust particles have any mass at all, gravity can pull them together. Who has a better argument and why?Penny, because objects with only a little mass are not affected by gravityEmma, because objects with smaller mass have more gravity acting on themEmma, because any two objects exert a gravitational force on each otherPenny, because dust particles in space are far from Earth so there is no gravity30s
- Q5Gordon is making a list of forces for his science class. Which of the following should Gordon NOT list as a force?MassFrictionGravityA push or pull30s
- Q6Ignoring mass and weight contributed by fuel, what happens when the space shuttle takes off and moves away from Earth?Its mass decreases and weight increases.Its mass increases and weight decreases.Its mass remains constant and weight increasesIts mass remains constant and weight decreases.30s
- Q7The law of universal gravitation states that any two objects in the universe that have mass, without exception,Attract each other.Repel each other.Combine to provide a balanced force.Create friction.30s
- Q8The forces acting on a falling apple areGravity and friction (air resistance).Mass and inertia.Gravity and inertia.Inertia and friction.30s
- Q9The gravitational force between two objects increases as massDecreases or distance increases.Increases or distance increases.Increases or distance decreases.Decreases or distance decreases.30s
- Q10The force of gravity on a person or object on the surface of a planet is calledMass.Terminal velocity.Free fall.Weight.30s
- Q11Which of the following is an example of a contact force?Magnetic forceGravitational forceNormal forceElectrical force30s
- Q12A force acting in the opposite direction of an object in motion. It slows down the motion or actually stops it.GravityFrictionBuoyantNormal30s
- Q13The sum of all forces acting on an object and directionBalanced ForceUnbalanced ForceContact ForceNet Force30s
- Q14What is the net force of an object that is not moving?Upward force100NDownward force0N30s
- Q15The type of forces that will cause an object to move or to change its motion (speed/ direction):Balanced forcesA net force of 0Unbalanced forcesApplied forces30s