2.8, 8.2
Quiz by Texel, Sarah J
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measure skillsfrom any curriculum
Measure skills
from any curriculum
Tag the questions with any skills you have. Your dashboard will track each student's mastery of each skill.
With a free account, teachers can
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
14 questions
Show answers
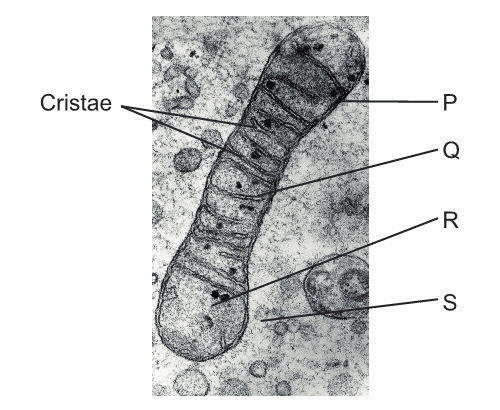
- Q1Where do glycolysis and electron transport occur?Glycolysis: P Electron Transport: RGlycolysis: R Electron Transport: RGlycolysis: R Electron Transport: QGlycolysis: S Electron Transport: Q120s
- Q2The graph shows the changes in lactate and pyruvate measured in an athlete’s blood during and following a mild exercise period as compared to the period before the exercise. What do these curves suggest?Before the exercise, there was no pyruvate produced because there was no cell respiration.After the exercise, the level of lactate decreased because there was enough pyruvate to be used for anaerobic cell respiration.During the exercise, there was not enough oxygen available for cell respiration, so the process was partly anaerobic.During the exercise, the level of lactate increased due to aerobic respiration.120s
- Q3This reaction occurs in mitochondria. What explains that this reaction enables energy to be converted into a usable form?The C6 compound is reduced and the energy resulting from the removal of one carbon is used to oxidize NAD+.Energy stored in the CO2 molecule will generate an electron gradient.The chemical energy stored in the C6 compound is used to reduce NAD+ allowing ATP production.The oxidized NAD+ will transfer the energy from the C6 compound to ATP.120s
- Q4From which substrate is the first carbon dioxide molecule released during cellular respiration?PyruvateCitrate (a C6 intermediate compound in the Krebs cycle)Acetyl CoAGlucose120s
- Q5Where in a eukaryotic cell does the Krebs cycle take place?Between the inner and outer membranes of the mitochondriaOn the surface of the cristaeIn the matrix of the mitochondriaIn the cytoplasm120s
- Q6The diagram shows anaerobic respiration in yeast cells. What would be produced at X?CO2 and H2OEthanol and CO2ATPLactate120s
- Q7What is the total number of ATP molecules used and produced during glycolysis?Used: 0 Produced:2Used: 4 Produced:4Used: 2 Produced:4Used: 2 Produced:2120s
- Q8Which process produces the most ATP per molecule of glucose?Glycolysis in a human liver cellAerobic respiration in a bacterial cellAnaerobic respiration in a yeast cellThe formation of lactic acid in a human muscle cell120s
- Q9What is chemiosmosis?H+ ions moving down a concentration gradient into the mitochondrial matrixCoupling of ATP synthesis to the electron transport and proton movementPhosphorylation of glucose in the mitochondrial matrixActivation of ATPase in order to synthesize ATP120s
- Q10In the mitochondrial electron transport chain, what is the last electron acceptor?NADH2OCO2O2120s
- Q11In the following diagram of a metabolic pathway, which letter represents acetyl CoA?BACD120s
- Q12Which is a reduction reaction?ATP changing to ADPMaltose changing to glucoseNADPH changing to NADPFAD changing to FADH2120s
- Q13What is the final electron acceptor of the ETC?oxygenATPNAD+glucose120s
- Q14At the end of glycolysis glucose is converted toATPCitrate2 acetyl CoA molecules2 pyruvate molecules120s