Air, Ocean Currents and Biogeochemical Cycles
Quiz by Devon Roesener
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measure skillsfrom any curriculum
Tag the questions with any skills you have. Your dashboard will track each student's mastery of each skill.
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
- Q1
Global air masses that carry moisture are known as . . .
continental air masses
polar air masses
tropical air masses
maritime air masses
30s - Q2
Global air masses that are dry are known as . . .
polar air masses
continental air masses
maritime air masses
tropical air masses
30s - Q3
A volume of air defined by its temperature and water vapor content.
climate
air mass
ocean current
air circulation
30s - Q4
A cool breeze coming off the ocean on a hot day.
sea breeze
ocean current
tidal wave
ocean breeze
30s - Q5
Intense storms that originate from the tropics and gain energy from the heat of the ocean.
hurricanes
tsunamis
tropical storms
tidal waves
30s - Q6
If the Earth did not rotate on its axis, the atmosphere would only circulate between . . .
the poles and the equator
the equator and 60 degree S latitude
only the equator
the equator and 60 degree N latitude
30s - Q7
The deflection of the air because of Earth's rotation is called the _____.
Coral effect
circulating air affect
Coriolis effect
Corolla affect
30s - Q8
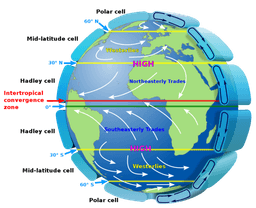
Closed circulation loop that begins at the equator to 30 degrees N or S of the equator.
Polar cell
Hadley cell
Westerly Cell
Ferrel Cell
30s - Q9
Air in these cells sinks over the highest latitudes and flows out towards the lower latitudes at the surface.
Westerlies
Hadley Cells
Polar Cells
Trade winds
30s - Q10
Motion of air between 30 and 60 degrees N and S of the equator.
Ferrel cells
Trade winds
Hadley cells
Southern westerlies
30s - Q11
Winds that blow east to west just N and S of the equator.
Doldrums
Westerlies
Easterlies
Trade winds
30s - Q12
A belt of the converging northeast and southeast trade winds causing an air uplift and producing clusters of convective storms.
trade winds
westerlies
horse latitudes
doldrums
30s - Q13
A belt of calm air and sea occurring in both the northern and southern hemispheres between the trade winds and the westerlies.
doldrums
hadley winds
ferrel winds
horse latitudes
30s - Q14
Has an impact on ocean temperatures, the speed and strength of ocean currents, the health of coastal fisheries, and local weather.
Pacific Ocean Current
California Current
El Nino
La Nina
30s - Q15
A climate pattern that describes the cooling of surface ocean waters along the tropical west coast of South America.
la nina
equatorial ocean current
Peru ocean current
el nino
30s