AP2 - Chapter 18 Exam Prep Quiz
Quiz by Katie Keesecker
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measure skillsfrom any curriculum
Measure skills
from any curriculum
Tag the questions with any skills you have. Your dashboard will track each student's mastery of each skill.
With a free account, teachers can
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
44 questions
Show answers
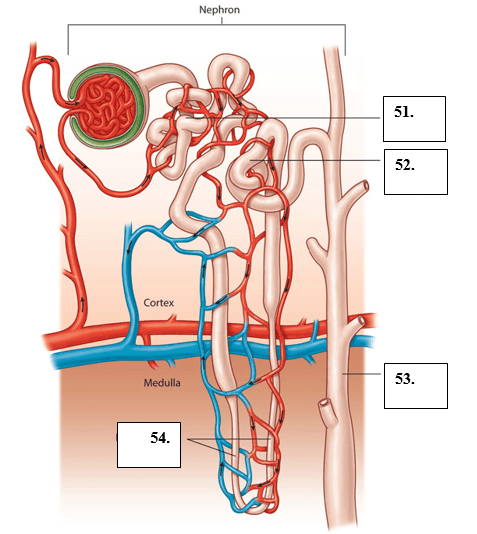
- Q1Identify #51proximal convoluted tubule30s
- Q2Identify #52distal convoluted tubule30s
- Q3Identify #53collecting duct30s
- Q4Identify #54loop of Henle30s
- Q5Identify #55kidney30s
- Q6Identify #56ureter30s
- Q7Identify #57urethra30s
- Q8Identify #58adrenal gland30s
- Q9Identify #59renal vein30s
- Q10Identify #60inferior vena cava30s
- Q11How does high blood pressure damage kidneys?The kidneys must work against high blood pressure to excrete filtrate, which places a strain on the glomerulushigh blood pressure drives filtrate formation at an accelerated rate, which wears out the glomerulushigh blood pressure increases pressure within the glomerulus, causing glomerular capillaries to burst30s
- Q12How much of the fluid filtered by both kidneys is reabsorbed by the body?50%33%99%80%30s
- Q13Most of the water, electrolytes, and nutrients are reabsorbed in theproximal convoluted tubuleglomerulusdistal convoluted tubuleloop of Henle30s
- Q14Aldosterone causes which of the following?increased sodium in urinedecreased potassium in urinedecreased urine outputincreased urine output30s
- Q15What is the most likely cause of protein in urine?high-protein diethigh pressure within the glomerulusproteinuria is a normal laboratory findingdamaged glomerular capillaries30s