B2.2 Compartmentalization - revision quiz
Quiz by L
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measure skillsfrom any curriculum
Tag the questions with any skills you have. Your dashboard will track each student's mastery of each skill.
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
- Q1
How does compartmentalisation by their internal membranes benefit eukaryotic cells?
The membranes help to keep the shape of the cell.
The membranes allow movement of the cytoplasm.
The membranes can form organelles.
The membranes increase the concentration of reactants in some organelles.
30s - Q2
Which organelle of eukaryotic cells produces polypeptides for secretion outside of the cell?
Ribosomes in the cytoplasm
Ribosomes on the rER
Lysosomes
The golgi apparatus
30s - Q3
Which organelle is visible in an electron microscope but not in a light microscope?
Nucleus
Golgi Body
Cell wall
Ribosome
30s - Q4
Why is the inner membrane of the mitochondrion folded into cristae?
To increase its surface area for ATP manufacture.
To allow more efficient gaseous exchange.
To be impermeable to protons.
To provide a larger surface area for the enzymes of the Krebs cycle.
30s - Q5
Which of the following cell components are not regarded as organelles?
Nucleus
Plasma membrane.
Cytoskeleton.
Mitochondria.
30s - Q6
Which of the following is the best description of an organelle?
The mitochondrion and chloroplast are organelles.
A membrane-bound component of a cell that has a particular function.
A cell component.
A part of a cell with a specific function.
30s - Q7
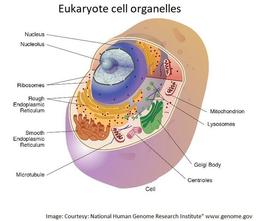
Why is the cell component in the image regarded as an organelle?
It is smaller than a cell.
It is a chloroplast.
It has a double membrane and is adapted for respiration.
It has a double membrane and is adapted for aerobic respiration.
30s - Q8
In which ways does the ultracentrifuge NOT aid in the research into individual organelles?
It can separate organelles based on their density.
It allows fractionation of cell components.
It can separate organelles based on their size.
It allows the researcher to separate molecules.
30s - Q9
The ultracentrifuge was invented by Nobel laureate Thomas Svedberg in 1920. It can be used to fractionate cell components. How did fractionation of cell components create progress in scientific research?
It allowed researchers to identify organelles.
It allowed researchers to separate individual organelles into suspensions.
It allowed researchers to identify molecular components of cells.
It allowed researchers to discover the function of chloroplasts.
30s - Q10
Which of the following happens in the nucleus but not in the cytoplasm?
Transcription of mRNA into polypeptides.
Modification of polypeptides for secretion.
Translation of mRNA into polypeptides.
Transcription of DNA to mRNA.
30s - Q11
Which of the following are advantages to the nucleus of eukaryotic cells being surrounded by a membrane?
Mutations can be prevented.
The genetic material can be kept discrete from the cell contents.
Translation can be controlled.
mRNA can be translated before it is transcribed.
30s - Q12
What are the roles of the Golgi apparatus?
Consuming vesicles for exocytosis.
Manufacturing polypeptides.
Forming vesicles for endocytosis.
Processing polypeptides for secretion.
30s