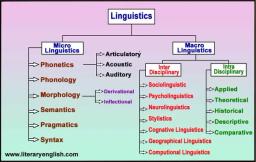
Branches of Linguistics
Quiz by Natasha Dvorin
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measure skillsfrom any curriculum
Tag the questions with any skills you have. Your dashboard will track each student's mastery of each skill.
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
- Q1
Major branches of traditional linguistics are
sociolinguistics, psycholinguistics, ethnolinguistics and pragmatics
linguistics of human language and linguistics of computer languages
transformational grammar and linguistic structuralism
phonetics, phonology, morphology, syntax, semantics and pragmatics
30s - Q2
One of the special branches of linguistics that deals with the study of meaning, reference, and truth.
Syntax
Pragmatics
Semantics
20s - Q3
The branch of linguistics deals with the study of words, their formation, and their relationship with other words within the same language.
Morphology
Phoneme
Phonology
Morpheme
20s - Q4
.... is a branch of linguistics that focuses on the production and classification of speech sounds.
Phonetics
Philology
Phonology
Phoneme
20s - Q5
The study of how we put words together to form sentences.
Semantics
Pragmatics
Syntax
20s - Q6
It studies how context helps to determine whether a particular utterance is appropriate or inappropriate, as well as how changes to context alter sentences’ meanings.
Stylistics
Pragmatics
Syntax
20s - Q7
Aspects associated with this subfield of linguistics include elements such as affixes, prefixes, suffixes, and circumfixes.
Phonology
Morphology
Syntax
Phonetics
20s - Q8
The study of acoustic results of different articulations.
Articulatory phonetics
Acoustic phonetics
Auditory phonetics
20s - Q9
This branch of linguistics leverages computer science to analyse, model, and produce speech.
Applied linguistics
Computational linguistics
Psycholinguistics
20s - Q10
The study of how listeners perceive and understand linguistic signals.
Acoustic phonetics
Articulatory phonetics
Auditory phonetics
20s - Q11
It studies the relationship between psychological processes and linguistic behaviour.
Applied linguistics
Neurolinguistics
Theoretical linguistics
Psycholinguistics
30s - Q12
It determines universal principles for studying languages and describes the general features of the language.
Applied Linguistics
Grammar
Theoretical linguistics
20s - Q13
It studies language used by different geographical and socio-cultural communities,
e.g., regional dialects.
Sociolinguistics
Comparative linguistics
Historical linguistics
20s - Q14
The study of sounds made with the articulators.
Auditory phonetics
Articulatory phonetics
Acoustic phonetics
20s - Q15
This branch is associated with identifying similarities and differences between languages that have a common origin.
Comparative linguistics
Historical linguistics
Sociolinguistics
20s