Ch.28 Climate
Quiz by Kate Downey
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measure skillsfrom any curriculum
Measure skills
from any curriculum
Tag the questions with any skills you have. Your dashboard will track each student's mastery of each skill.
With a free account, teachers can
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
35 questions
Show answers
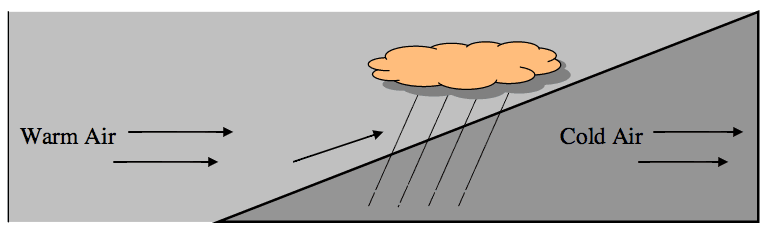
- Q1What type of front is shown below?stationary frontoccluded frontwarm frontcold front30s
- Q2What best describes a maritime Tropical air mass?cold and wetwarm and wetcold and drywarm and dry30s
- Q3What kind of weather does a cold front usually bring?thunderstormsovercast conditionsfogwarm weather30s
- Q4Which of the following is the best definition for climate?The day to day changes in the atmosphereThe average weather over a long period of time and over large areasThe state of the atmosphere across the worldNone of the options are correct.30s
- Q5Which type of climatic zone experiences hot and wet conditions all year?tropics zonetemperate zonepolar zone30s
- Q6Which of the following describes an air mass with the symbol cP?cold and drywarm and wetwarm and drycold and wet30s
- Q7How does a warm front form?Cold air moves under warm air and pushes it up.Warm air moves over cold air and replaces it.Warm air becomes caught between cold air masses.Two air masses meet and stay separated.30s
- Q8Which of the following is the cause of the change of seasons?the prevailing windsthe distance of a place from the Equatorthe tilt of the Earth’s axisthe rotation of the Earth30s
- Q9Which of the following explains why one side of a mountain usually has more precipitation than the other side?Temperatures are higher on one side of a mountain than on the other.Mountains force air to rise, and air cools and releases moisture as it rises.The land on one side is more green and lush than the other.The atmosphere gets denser as elevation increases.30s
- Q10Why does the equator experience about the same temperatures year-round?It tilts toward the sun and gets much more direct solar energy.It has no mountains to affect its climate.It has no prevailing winds.The sun’s rays strike the equator at about the same angle all year.30s
- Q11The windward side of a mountain usuallyhas warm, sinking air.is a desert.has no precipitation.is lush and green.30s
- Q12Which is not one of the major climate zones?temperaterainforestpolartropical30s
- Q13What is the latitude range of the polar zone?0 - 30 degrees60 - 90 degrees30 - 60 degrees0 degrees30s
- Q14How are climate zones determined?longitudelatitude30s
- Q15Weather can change drastically day to day?FalseTrue30s