Continental Drift and Sea-Floor Spreading
Quiz by Alexander Shannon
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measure skillsfrom any curriculum
Measure skills
from any curriculum
Tag the questions with any skills you have. Your dashboard will track each student's mastery of each skill.
With a free account, teachers can
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
14 questions
Show answers
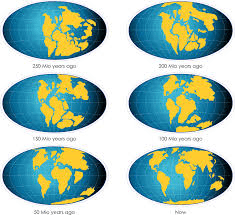
- Q1is the hypothesis that all the continents had once been joined together in a single landmass called Pangaea and drifted to their present day positionsContinental drift theory30s
- Q2Crust and the uppermost part of the mantle (tectonic plates)lithosphere30s
- Q3huge moving slabs of solid rocktectonic plates30s
- Q4region below the lithosphere on which the tectonic plates moveasthenosphere30s
- Q5theory that Earth's lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates and these plates move slowly on top of the asthenospherePlate Tectonic Theory30s
- Q6all the continents were once joined together in this supercontinentPangaea30s
- Q7-mountains ranges in South America and Africa line upEvidence from landforms30s
- Q8-fossils of the Glossopteris (fern-like) plant found on many different continentsEvidence from Fossil30s
- Q9-fossils of a tropical plant found near the Artic OceanEvidence from Climate30s
- Q10German scientist that proposed the theory of Continental Drift around 1910-1915Alfred Wegener30s
- Q11A circulation pattern in which material is heated and rises in one area, then cools and sinks in another area, flowing in a continuous loopConvection Currents30s
- Q12the process by which new oceanic lithosphere forms as magma rises and cools at the mid-ocean ridgesea-floor spreading30s
- Q13a chain of mountain ranges on the ocean floor where new oceanic crust formsMid-ocean ridge30s
- Q14is the process by which denser oceanic lithosphere sinks back into the asthenosphere to melt and become magmasubduction30s