Cycles in nature
Quiz by Trina Hope-Ross
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measure skillsfrom any curriculum
Measure skills
from any curriculum
Tag the questions with any skills you have. Your dashboard will track each student's mastery of each skill.
With a free account, teachers can
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
24 questions
Show answers
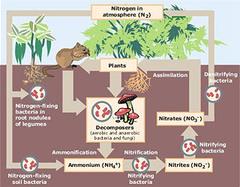
- Q1nitrogen in the atmosphere (N2) is converted into usable nitrogen in the form of ammonia (NH3) or (NH4)Nitrogen Fixation30s
- Q2CO2 is taken from the air & trapped into food (glucose)Photosynthesis30s
- Q3Break down dead animals & plants (decompose) for energy & recycle back Carbon and NitrogenDecomposers30s
- Q4CO2 is returned to the atmosphere when food (Glucose) is broken down for energyCellular respiration30s
- Q5process is done by bacteria that live in plant roots/ convertingNitrification (N2 -> NH3) done by...30s
- Q6recycle nutrients essential to all organisms/ both move from the soil to the roots of plants, then are ingested by animals, and returned to the environment through decompositionBoth cycles:30s
- Q7plants take it in and use it to make sugar, then animals eat the plants and use the sugar/ some is released as the carbon dioxide we exhale/ plants use carbon to make their foodCarbon30s
- Q8makes up about 78% of the airNitrogen30s
- Q9the process of converting nitrogen into compounds that can be used by plants and animalsNitrogen cycle30s
- Q10Used in Genetic Material and ProteinsUses for Nitrogen30s
- Q11process of burningcombustion30s
- Q12-matter cannot be created or destroyed, only changed from one form to anotherConservation of Matter30s
- Q13Evaporation of water from the leaves of a plantTranspiration30s
- Q14long-term significant change in the weather patterns of an areaClimate Change30s
- Q15a colorless, odorless gas produced by burning carbon and organic compounds and by respirationCarbon Dioxide30s