Electromagnetic Induction
Quiz by MILI SANTHOSH
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measure skillsfrom any curriculum
Measure skills
from any curriculum
Tag the questions with any skills you have. Your dashboard will track each student's mastery of each skill.
With a free account, teachers can
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
15 questions
Show answers
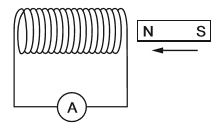
- Q1As a magnet is moved into the coil of wire as shown, there is a small reading on the sensitive ammeter. Which change increases the size of the reading?unwinding some of the turns of wiremoving the opposite pole into the coilpulling the magnet out of the coilpushing the magnet in faster60s
- Q2A student moves a magnet into a coil of wire as shown in the diagram. The coil of wire is connected to a sensitive ammeter. Which change does not produce an increase in the reading?increasing the resistance of the ammeterincreasing the strength of the magnetincreasing the number of turns on the coilincreasing the speed of the magnet60s
- Q3A current is produced when a wire is moved between two magnets as shown. Which device uses this effect?a batteryan electromagneta generatora motor60s
- Q4A bar magnet is pushed into one end of a long coil connected to a sensitive meter. Which of the following affects the magnitude of the deflection of the meter?the speed with which the magnet enters the coilthe direction in which the coil is woundwhich pole of the magnet enters firstwhich end of the coil is used60s
- Q5The diagram shows the N-pole of a magnet moving into, and out of, a coil of wire. This movement produces a current in the coil of wire. The current produces a magnetic pole at X. Which pole is produced at X when the magnet is moved in and when it is moved out?N pole when the magnet is moved in, S pole when the magnet is moved out.N pole when the magnet is moved in, N pole when the magnet is moved out.S pole when the magnet is moved in, N pole when the magnet is moved out.S pole when the magnet is moved in, S pole when the magnet is moved out.60s
- Q6A magnet is moved towards a coil of insulated wire. A voltmeter connected across the coil shows a positive reading. What produces a higher reading on the voltmeter?moving the magnet away from the coil at a slower speedmoving the magnet towards the coil at a faster speedmoving the magnet towards the coil at a slower speedmoving the magnet away from the coil at the same speed60s
- Q7The electromotive force (e.m.f.) induced in a conductor moving at right-angles to a magnetic field does not depend uponthe resistance of the conductor.the strength of the magnetic field.the length of the conductor.the speed of the conductor.60s
- Q8A small coil is connected to a galvanometer G, as shown. When a magnet is allowed to fall towards the coil, the galvanometer pointer gives a momentary deflection to the right of the zero position. The magnet moves through the coil. What happens to the galvanometer pointer as the magnet falls away from the coil?It gives a momentary deflection to the left.It gives a momentary deflection to the right.It gives a continuous reading to the right.It gives a continuous reading to the left.60s
- Q9A magnet is pushed slowly into a coil and there is a current in the coil in the direction shown. The magnet is then pulled out quickly from the same end of the coil. What happens to the direction and the size of the current?direction unchanged; size increaseddirection reversed; size decreaseddirection reversed; size increaseddirection unchanged; size decreased60s
- Q10A magnet is pushed horizontally towards a coil of wire, inducing an e.m.f. in the coil. In which direction does the induced e.m.f. make the coil move?towards the magnetupwardsaway from the magnetdownwards60s
- Q11A conductor is moving horizontally across a vertical magnetic field. An e.m.f. is induced in the conductor. No deflection is seen on the ammeter. What is the reason for this?The ammeter is not between the poles.The conductor is not cutting field lines.The poles are too close together.The conductor is moving too slowly.60s
- Q12The diagram shows how a magnet and a coil may be used to induce an electric current. How could the ammeter reading be increased?Turn the magnet round, then move the coil.Use a coil with more turns.Put a resistor in series with the ammeter.Move the coil more slowly.60s
- Q13A small coil is connected to a sensitive ammeter. The ammeter needle can move to either side of the zero position. As the magnet falls towards the coil, the ammeter needle moves quickly to the right of the zero position. The magnet moves through the coil. How does the ammeter needle move as the magnet falls away from the coil?It moves quickly to the right of the zero position and then returns to zero.It gives a steady reading to the right.It does not moveIt moves quickly to the left of the zero position and then returns to zero.60s
- Q14A permanent magnet moving up and down on the end of a spring induces an e.m.f. in a coil. Which factor, on its own, would decrease the maximum value of the induced e.m.f.?increasing the number of turns in the coilraising the support of the springraising the coilincreasing the strength of the magnet60s
- Q15A student pushes the N-pole of a bar magnet into the end Q of a long solenoid and observes a deflection to the right on the sensitive ammeter. What will produce a deflection in the same direction?pulling the N-pole out of end Qpushing the N-pole into end Ppushing the S-pole into end Ppulling the S-pole out of end P60s