Force & Motion CBA Review
Quiz by Grade 6 Science - Texas Education Agency
Grade 8
Science (2017)
Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS)
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measure skillsfrom any curriculum
Measure skills
from any curriculum
Tag the questions with any skills you have. Your dashboard will track each student's mastery of each skill.
With a free account, teachers can
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
15 questions
Show answers
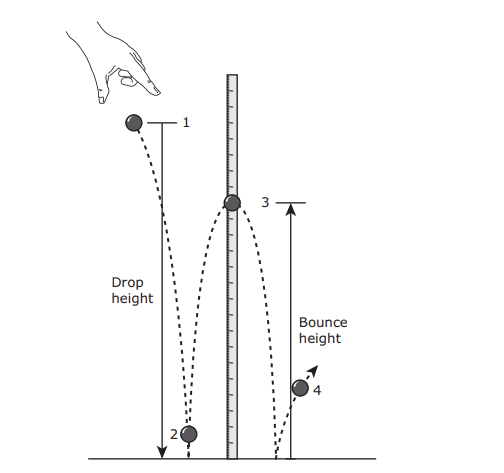
- Q1In the classroom demonstration shown below, a rubber ball is dropped from Position 1. The ball bounces as shown. At which of these positions does the ball have both the greatest kinetic energy and the least potential energy?Position 1Position 2Position 4Position 3300s
- Q2A bus travels 20 km in 30 minutes. What is the average speed of the bus?30 km/h40 km/h20 km/h50 km/h300s
- Q3A student runs two times around a running path at a local park. Each lap is 3 km. The student completes the first lap in 20 minutes. The student then sits on a bench and rests for 5 minutes before completing the second lap in 25 minutes. Which graph best represents the student’s motion?#texas/3b333deb-3d2d-4f0a-bead-bafc9856e79e/A.png#texas/3b333deb-3d2d-4f0a-bead-bafc9856e79e/C.png#texas/3b333deb-3d2d-4f0a-bead-bafc9856e79e/D.png#texas/3b333deb-3d2d-4f0a-bead-bafc9856e79e/B.png300s
- Q4A bicycle rider is traveling up a hill. When the rider reaches the top of the hill, she stops to rest. Then she travels down the hill. The diagram shows the rider in the three different positions. Which of these correctly describes the potential energy and the kinetic energy of the bicycle rider?As the rider reaches the bottom of the hill, her kinetic energy and her potential energy decrease.When the rider is at the top of the hill, her potential energy is the greatest, and her kinetic energy is the least.When the rider goes down the hill, her potential energy increases, and her kinetic energy decreases.As the rider moves up the hill, her kinetic energy increases, and her potential energy decreases.300s
- Q5A student kicks a soccer ball three times. Another student records the distance, the amount of time the ball travels, and the average speed in the table shown below. How many seconds did it take for the ball to travel 30 m during Kick 3?1.5 s2.0 s1.0 s0.5 s300s
- Q6Four students were asked to classify the activities of the people in the picture below as examples of either potential or kinetic energy. Which student correctly classified the activities?#texas/97806e28-19b5-4a15-9f31-eb49e51af5a5/A.png#texas/97806e28-19b5-4a15-9f31-eb49e51af5a5/C.png#texas/97806e28-19b5-4a15-9f31-eb49e51af5a5/D.png#texas/97806e28-19b5-4a15-9f31-eb49e51af5a5/B.png300s
- Q7A hobbyist collected data about the motion of a toy train on a straight track and then recorded the data in the graph below. Which of these accurately describes the motion of the toy train?The toy train speeds up while going forward and then slows down.The toy train moves forward at a constant speed, slows down, and then stops.The toy train moves forward at an increasing speed, stops, and then moves forward.The toy train slows down while going forward and then moves backward.300s
- Q8The three vehicles shown below are all traveling at a speed of 15 m/s, but only the pickup truck has a changing velocity. The pickup truck has a changing velocity because the pickup truck —is traveling in the opposite direction from the other two vehiclesneeds a large amount of force to moveis traveling on a curve in the roadcan accelerate faster than the other two vehicles300s
- Q9The diagram below shows a boat moving north in a river at 3 m/s while the current in the river moves south at 1 m/s. How will the boat be affected if it enters a part of the river where the current is moving south at 2 m/s?The boat will stop.The boat will move slower.The boat will move faster.The boat will move to the west.300s
- Q10During a demonstration of Newton’s laws of motion, a student used the setup shown in Figure 1. The student flicked the index card with a fingertip, and the coin fell straight down into a plastic cup as shown in Figure 2. Which of these best explains why the coin fell straight down into the cup instead of remaining on the index card?Moving the card applied an action force on the coin. Since the card was gone, gravity applied a reaction force on the coin.The card had less mass than the coin, so a smaller force of gravity acted on the card. The larger force of gravity on the coin made it fall.The coin was at rest until the card was removed, so it tended to remain in the same location. Once the card was gone, the unbalanced force of gravity caused the coin to fall.The acceleration of the coin falling into the cup was equal and opposite to the acceleration of the card.300s
- Q11Which of the following best describes the velocity of an object?30 m/s30 m/s$^2$30 m/s east30 m east300s
- Q12A student jumps off a sled toward the west after it stops at the bottom of an icy hill. Based on the law of action–reaction, in what direction will the sled most likely move as the student jumps off?EastNorthSouthWest300s
- Q13NASA’s space shuttle program was active from 1981 until 2011. The photograph shows rockets carrying a space shuttle off the launchpad. How can Newton’s law of action–reaction best be applied to explain the movement of a rocket?As the fuel burns, the rocket moves fasterAs the fuel burns, the mass of the rocket decreases.As the fuel burns, gases move out of the rocket and reduce air resistance.As the fuel burns, gases push against the rocket, moving it upward.300s
- Q14Two cars with different masses travel at the same speed down a hill toward a stop sign. What will happen when both cars apply brakes at the same time to stop?The car with the smaller mass will take longer to stop than the car with the larger mass.The car with the larger mass will maintain its velocity while traveling down the hill.The car with the smaller mass will require less force to stop than the car with the larger mass.The car with the larger mass will have less inertia than the car with the smaller mass.300s
- Q15The picture shows an aerialist walking on a tightrope holding a balance bar. An action-reaction pair of forces exist betweenthe aerialist's feet and the ropethe aerialist's arms and legsthe two end of the ropethe rope and the balance bar300s