HDHS Trilogy B1 Checkpoint quiz: Cell structure and transport
Quiz by Alexandra Gill
GCSE (AQA)
Combined Science: Trilogy (ARCHIVED)
English National Curriculum
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measures 8 skills from
Measures 8 skills from
With a free account, teachers can
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
14 questions
Show answers
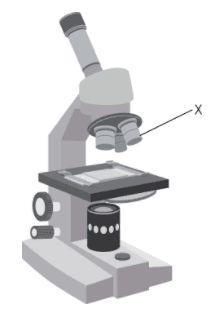
- Q1The diagram shows a light microscope. Name the part of the microscope labelled X.objective lenscoarse focuseyepiecestage30s4.1.1.5
- Q2What is the function of the mitochondria in a cell?site of protein synthesissite of aerobic respirationcontrols the activities of the cellsite of photosynthesis30s4.1.1.2
- Q3Which adaptation is a feature of a muscle cell?they contain a large nucleusthey can store glycogenthey are very longthe acrosome contains digestive enzymes30s4.1.1.3
- Q4Which adaptation is a feature of an exchange surface in large animals?the exchange surface has a poor blood supplythe exchange surface has a small surface areathe exchange surface has a thick membranethe exchange surface is well ventilated30s4.1.1.3
- Q5A scientist viewed a bacterial cell under a microscope. The image measured 6.25 mm and the actual cell was 25 µm. Calculate the magnification the scientist used.× 156.25× 156 250× 250× 0.2530s4.1.1.5
- Q6The diagram shows a bacterial cell. What is the function of the structures labelled X?X codes for very specific features such as antibiotic resistanceX is responsible for protection of the bacterial cellX is responsible for movement of the bacterial cellX is the site of most of the chemical reactions that occur in the bacterial cell30s4.1.1.1
- Q7Which row shows the conditions that would increase the rate of diffusion?DACB30s4.1.3.1
- Q8What would happen if you placed a cell in a hypertonic solution?solutes would enter the cell from the solutionwater would enter the cell from the solutionsolutes would enter the solution from the cellwater would enter the solution from the cell30sRP.2
- Q9Which of these processes is an example of active transport?uptake of carbon dioxide through stomata in the leafrelease of oxygen through stomata in the leafabsorption of mineral ions by plant rootsabsorption of water by plant roots30s4.1.3.3
- Q10The table shows the surface areas and volumes of four different animals A, B, C and D. Which has the largest surface area to volume ratio?CABD30s4.1.3.2
- Q11The table shows some features present in bacterial and plant cells. Which row shows the features that are common to both bacterial and plant cells?ACBD30s4.1.1.1
- Q12Which statement is the best explanation of why root hair cells do not contain chloroplasts?root hair cells have lost most of their internal structuresroot hair cells are composed of dead tissueroot hair cells have no access to lightroot hair cells have no room for chloroplasts due to the large permanent vacuole30s4.1.1.3
- Q13A plant has been flooded with sea water and wilts. After the plant has been watered with fresh water it quickly recovers. What would have been the appearance of the plant cells when exposed to sea water?plant cells would have burstplant cells would be flaccidplant cells would be plasmolysedplant cells would be turgid30s4.1.3.2
- Q14Where in the body are you most likely to find cells containing lots of mitochondria?kidneyhairblood capillariesalveoli30s4.1.1.2