HDHS Trilogy C3 Checkpoint quiz: Structure and bonding
Quiz by Alexandra Gill
GCSE (AQA)
Combined Science: Trilogy (ARCHIVED)
English National Curriculum
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measures 6 skills from
Measures 6 skills from
With a free account, teachers can
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
9 questions
Show answers
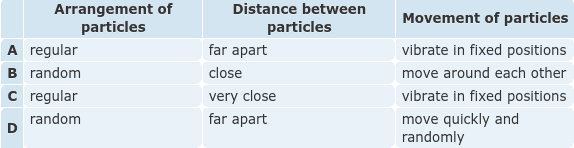
- Q1The table shows some properties of the particles in a solid, liquid, and gas. Which row shows the properties of particles in a liquid?ADBC60s5.2.2.1
- Q2The table shows a list of different substances with their boiling points. Which sequence shows the order of boiling points from lowest to highest?AEBDCCDBEAEABDCEACDB60s5.2.2.1
- Q3Name the process that turns a gas into a liquid.condensationboilingcondensationmelting60s5.2.2.1
- Q460s5.2.1.4
- Q5Ethene is a useful substance that can form polymers. It has a melting point of 169°C and a boiling point of 104°C. At which temperature would ethene be a liquid?0 °C170 °C100°C105°C60s5.2.2.1
- Q6Which sentence describing different types of bonding is correct?An ionic bond is formed when two atoms share a pair of electrons.When two ions are attracted to one another they form a covalent bond.Ionic bonding is when two oppositely charged ions are held together by electrostatic attraction.Covalent bonding occurs when positive ions are held together by delocalised outer electrons.60s5.2.1.2
- Q760s5.2.1.3
- Q8Which sentence explains why metals can form alloys with different properties?Electrostatic attraction between the nuclei and the electrons acts throughout the structure.Outer electrons are able to move freely throughout the giant structure.Different sized metal atoms affect the ability of the layers in the metal’s structure to slide over one another.Layers of atoms in the metal’s structure can slide over one another.60s5.2.1.5
- Q9Which one of these would have a giant covalent structure?A colourless gas at room temperatureA solid with a melting point of 801°C that conducts electricity when molten and dissolved.A solid with a boiling point of 2950°C that cannot conduct electricityA brown liquid at room temperature60s5.2.2.6