Homework 4 Term 2 Classical Rome
Quiz by christine degregorio
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measure skillsfrom any curriculum
Measure skills
from any curriculum
Tag the questions with any skills you have. Your dashboard will track each student's mastery of each skill.
With a free account, teachers can
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
7 questions
Show answers
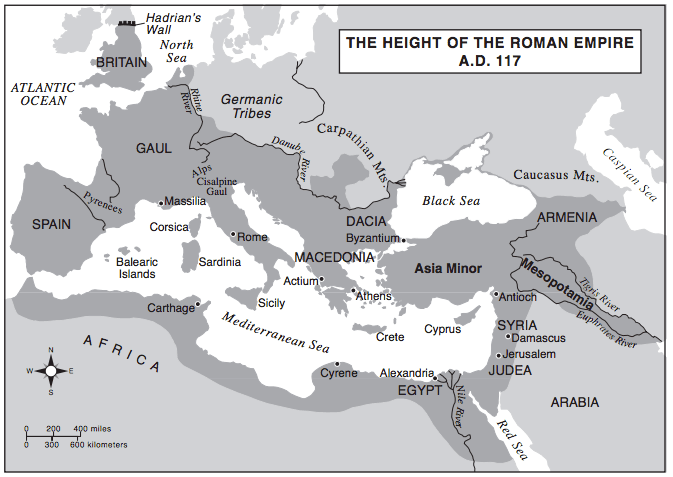
- Q1Which statement is best supported by the information on this map?Alexandria served as the eastern capital of the Roman Empire.The Roman Empire extended over three continents.Rivers kept invaders out of the Roman Empire.Carthage was eventually destroyed by the Romans.300s
- Q2Based on the information provided by this map, which body of water was most likely the center of Roman trade?Red SeaMediterranean SeaAtlantic OceanBlack Sea300s
- Q3Purposes and Kinds of Roman Roads Why did the Romans build roads? The Romans considered a well-organized and efficient transportation system a basic element of proper administration; i.e. an indispensable element in creating and maintaining the Roman state. The earliest highways or main roads were constructed for the use of the military, and their economic benefit for civilians was a later byproduct and not the main reason for their creation. The military nature of the roads continued to be essential as Romans expanded into territory outside Italy. In the province of Arabia Petraea (which included what is now Jordan), the movement of troops and ease of communication for the army and Roman administration were the primary reasons for construction of the Via Nova, one of the many viae militares or military roads built in conquered provinces. However, smaller, shorter, and less well-constructed local roads (actus) or tracks (callis) also increased in territory after it was brought under Roman control. Nevertheless, the main public highways (viae publicae) normally began as military roads and only gradually evolved into civilian conduits [passageways]. Source: Virtual Karak Resources Project, An Appalachian College Association (adapted) from the NYS Global History and Geography Regents Exam, January 2012 In which region would an archaeologist be most likely to find evidence of Roman Roads?Mongolia(2) Western EuropeSouth AsiaSub-Saharan Africa300s
- Q4What is the point of view of the author of this excerpt?(1) The Romans were the best road builders during the Classical period.(2) Neglect of the Roman road system led to the collapse of the empire.(3) The Roman economy would not have prospered if it were not for the roads in the empire.Roman roads were built primarily to keep order in the empire.300s
- Q5Where was this document written?Gupta EmpireAncient Egypt1. Ancient GreeceAncient Rome300s
- Q6What was the purpose of these “Tables?”To punish lower classes and slaves3. To show favoritism to the patricians4. To remove freedom from the peopleTo have laws binding both plebeians and patricians300s
- Q7Many world historians would argue that the aquaducts shown in the photograph above exemplify Rome’s attempt to. Build massive structures to create religious unity within a multicultural empireUtilize slave labor in their armiesConnect their world to the Far East and the Han dynastyDevelop monumental architecture as a unifying force300s