Human digestive system
Quiz by sheeba charles
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measure skillsfrom any curriculum
Measure skills
from any curriculum
Tag the questions with any skills you have. Your dashboard will track each student's mastery of each skill.
With a free account, teachers can
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
14 questions
Show answers
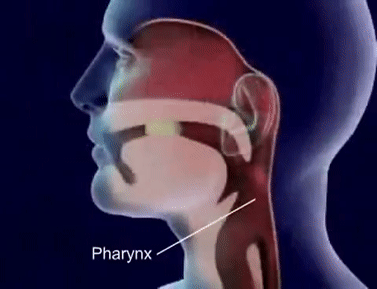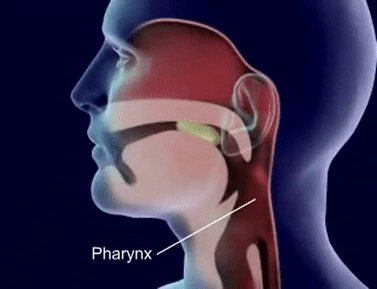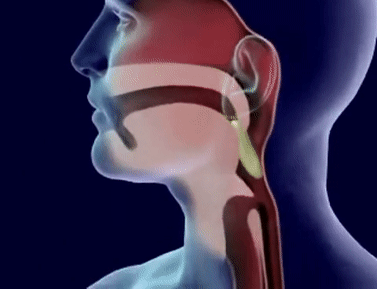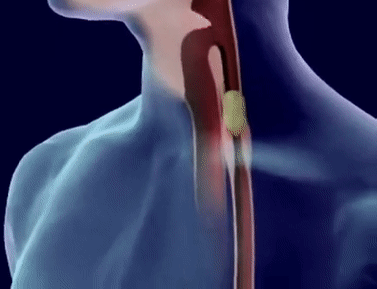
- Q1The structure which prevents entry of food into the windpipe during swallowing in mammals is:EpiglottisGlottisPharynxLarynx30s
- Q2Glottis is a structure which:Allows air to enter in trachea.Produces sound as air is forced through it.Prevents entry of food into windpipe during swallowing food.Allows food to pass into oesophagus.30s
- Q3Trypsinogen is produced by:StomachPancreasLiverDuodenum30s
- Q4When gall bladder of a man is removed:Fat digestion is not possible.Acidity continues in the duodenum.All of the aboveThe effect of pancreatic juice on food is impaired.30s
- Q5When a piece of bread is chewed, it tastes sweet because:The taste buds are stimulated by chewing.It does not taste sweet.Saliva converts starch into maltose.The sugar contents are drawn out.30s
- Q6Functional units of absorption of digested food are:Crypts of LieberkuhnPeyer's patchesBrunner's glandVilli30s
- Q7In which part of gut, proteins ultimately degraded to amino acids?Small intestineColonCaecumStomach30s
- Q8Pancreatic juice takes part in digestion of:Proteins onlyProteins and fatsProteins, fats and carbohydratesProteins and carbohydrates30s
- Q9Small intestine is distinguishable into 3 parts, a 'U' shaped____, a long coiled middle portion ____ and a highly coiled ____.Caecum, duodenum, ileumJejunum, duodenum, ileumIleum, jejunum, duodenumDuodenum, jejunum, ileum30s
- Q10How do nutrients, absorbed by the small intestine, travel to the individual cells of the human body?The body cells send nerve impulses indicating a lack of nutrients to the small intestine, and the small intestine sends the nutrients back to the cells.The nutrients are absorbed from the small intestine into the blood and move through the circulatory system to the body cells.The small intestine forces the nutrients into the kidneys, where the nutrients are then dissolved in fluids used by the body cells.The nutrients move from the small intestine directly to the liver and then move through the lymphatic system to the body cells.30s
- Q11If the bile-pancreatic duct is blocked then which of the following will not be affected?Digestion of proteinsEmulsification of fatsDigestion of starchLevel of blood glucose30s
- Q12During prolonged fasting,First fats are used up, followed by carbohydrates from the liver and muscles and proteins in the end.First lipids, followed by proteins and carbohydrates towards the end.First carbohydrates are used up, followed by fat and proteins towards the end.None of the above30s
- Q13Pancreatic cancer is an especially dangerous disease in people because the pancreas isThe site of synthesis for all of the essential amino acids.An organ in which many different kinds of digestive enzymes are manufacture.The organ that produces and stores bile.One of the organs through which food must pass on its way to the colon.30s
- Q14Colostomy is the removal of large parts of the colon. The principal effect of a colostomy is:DiarrhoeaConstipationKwashiorkor and marasmusIncreased loss of bile pigments30s