Matter, Mixtures, Compounds, & Elements Mastery Check
Quiz by Amanda Rogers
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measures 3 skills from
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
- Q1
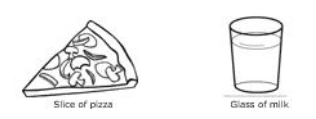
The illustration shows two kinds of matter. Which BEST explains how pizza differs from milk?
Pizza is a suspension, and milk is a solution.
Both are solutions; pizza’s components can be seen, and milk’s components cannot be seen.
Pizza is a mixture, and milk is a compound.
Both are mixtures; pizza is heterogeneous, and milk is homogeneous.
30sS8P1a - Q2
Students were asked to create and sort models of classified matter into pure substances and mixtures. Which statement correctly explains how the molecules in the illustration could be sorted based on their characteristics?
Sample X is the only example of a pure substance, because it is the only sample with only one type of element.
Samples V and Y are mixtures, because they are made of multiple substances that are not chemically combined.
Samples U and W are classified as mixtures, because the molecules are chemically combined in these samples.
Samples U, V, and W are examples of pure substances, because there are multiple unique substances in the samples.
30sS8P1a - Q3
Kala wanted to classify common household materials as pure substances and mixtures. She collected as many things from around her house as possible and made two lists. Kala’s friend thinks that she made a mistake.
What change can Kala make to her list that will correct her mistake?
Kala should place sugar in the list of mixtures, and butter in the list of pure substances.
Kala should place baking soda in the list of mixtures, and chalk in the list of pure substances.
Kala should place milk in the list of mixtures, and shampoo in the list of pure substances.
Kala should place milk in the list of mixtures, and chalk in the list of pure substances.
30sS8P1a - Q4
Ellie was comparing samples of substances to determine if they were a pure substance or a mixture. Ellie classified Samples A and B as mixtures and Sample C as a pure substance.
Is Ellie’s classification correct? Why or why not?
She is correct because Samples A and B both contain Sample C and therefore are considered mixtures.
She is correct because Samples A and B both contain different substances to make mixtures and sample C is made up of one substance to be a pure substance.
She is incorrect because Sample B contains different types of substances and should be classified as a pure substance.
She is incorrect because Sample A contains only one type of substance and should be classified as a pure substance.
30sS8P1a - Q5
An unknown substance is a liquid and is red in color.
How can you determine if the unknown is a mixture or a pure substance?
Look at a small sample of the substance under a microscope to see if there are any chemical bonds, indicating the substance is a compound.
Weigh the liquid, measure the volume, and calculate the density, and if the density is greater than 1.0 g/ml the liquid is a pure substance.
Heat the liquid in order to determine the boiling point, and if the boiling point is less than 100 °C the liquid is a mixture.
Pour a small amount of the liquid onto a clean surface and wait to see if water evaporates leaving a solid indicating that the substance is a mixture.
30sS8P1a - Q6
In the water cycle, water molecules absorb thermal energy from the Sun, causing them to evaporate from lakes and oceans and rise into the atmosphere. Eventually, they form clouds and then precipitation.
Which statement describes the activity of the water molecules in this process?
The molecules separate into atoms of hydrogen and oxygen gas. Because these atoms are smaller than the surrounding air particles, they rise and reach cooler temperatures, where they rejoin to form water molecules.
The molecules at the surface of the water reach the boiling point when they move so fast that they break the surface tension and turn into steam. The steam rises to high altitudes, where it cools and condenses into clouds.
The molecules at the surface of the water reach the boiling point and separate into atoms of hydrogen and oxygen gas. Because these atoms are smaller than the surrounding air particles, they rise and reach cooler temperatures, where they rejoin to form water molecules.
The molecules move so fast that they break the bonds holding them together and turn into a gas. As they rise to cooler temperatures, they slow down and rejoin to form water droplets.
30sS8P1b - Q7
On chilly mornings, water vapor may cool to form frost on grass and windows. It goes directly from a gas to a solid through a process called deposition.
Which sequence of boxes represents the change in the movement of particles of water vapor as it deposits?
Box O to box N to box M.
Box M to box O.
Box O to box M.
Box M to box N to box O.
30sS8P1b - Q8
The diagram represents water molecules at 0 ⁰C.
How should the model be changed to show these water molecules at -5 ⁰C?
30sS8P1b - Q9
Alex’s teacher showed him a model of gas particles in a sealed container.
How should Alex change the model to show the particles of this gas at a higher temperature?
30sS8P1b - Q10
You are planning and carrying out investigations to distinguish between chemical and physical properties of sugar.
Which of the following techniques demonstrates a chemical property of sugar and why?
Mixing the sugar with crushed ice will cause the ice to melt, which demonstrates a chemical property because the result is a totally different substance than what you started with.
Mixing the sugar with food coloring will change the color of the sugar, which demonstrates a chemical property because the result is a totally different substance than what you started with.
Mixing the sugar with milk produces a white sweet mixture, which demonstrates a chemical property because the result is a totally different substance than what you started with.
Mixing the sugar with sulfuric acid produces a lot of heat, some gas bubbles, and a sticky black substance which demonstrates a chemical property because the result is a totally different set of substances than what you started with.
30sS8P1c - Q11
Which state of matter has the highest density and the largest amount of chemical potential energy?
gas
solid
liquid
plasma
30sS8P1c - Q12
Relate the changes in molecular motion of particles as they change from solid to liquid to gas.
As the phase changes occur, the freedom of motion of the particles compresses.
As the phase changes occur, the freedom of motion of the particles increases.
As the phase changes occur, the freedom of motion of the particles is constant.
As the phase changes occur, the freedom of motion of the particles decreases.
30sS8P1b - Q13
Elaborate on the reason(s) that matter is said to move even as in a solid state
The particles have sufficient energy to become an ionized gas and are in the most common state of matter in the universe.
The particles are bound through intermolecular forces but are able to move past each other with relative freedom.
The particles are not able to move out of their positions relative to one another, but do have small vibrational movements.
The particles are not bound to one another, move quickly, have a low density, and are able to spread apart from one another if unconstrained.
30sS8P1b - Q14
Which of these would best describe the outcome of increasing the kinetic energy of the molecules in the above picture?
The temperature will remain unchanged.
The temperature would fluctuate up and down.
The temperature will decrease.
The temperature will increase.
30sS8P1b - Q15
From the list below, determine which properties are for compounds.
I. It takes a large amount of energy to separates the elements of a compound.
II. The proportions of the elements in a compound are always fixed.
III. It is easy to separate the elements of a compound.
IV. The elements/components of a compound do not retain their individual properties.
I, II & IV
II, III, & IV
I & II
II & III
30sS8P1a