Metabolism Quiz Ch.8 AP Biology
Quiz by Clifford Traylor
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measure skillsfrom any curriculum
Tag the questions with any skills you have. Your dashboard will track each student's mastery of each skill.
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
- Q1
Which of the following describe(s) some aspect of metabolism?
C. control of enzyme activity
B. breakdown of macromolecules
A & B only
A, B and C
A. synthesis of macromolecules
120s - Q2
Which term most precisely describes the cellular process of breaking down large molecules into smaller ones?
catabolism
catalysis
dehydration
metabolism
anabolism
120s - Q3
Which of the following statements correctly describe(s) catabolic pathways?
All the answers are correct
They consume energy to build up polymers from monomers.
They do not depend on enzymes.
They lead to the synthesis of catabolic compounds.
They release energy as they degrade polymers to monomers
120s - Q4
Which of the following is a statement of the first law of thermodynamics?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed
Energy cannot be transferred or transformed.
The entropy of the universe is decreasing.
Kinetic energy is stored energy that results from the specific arrangement of matter.
the entropy of the universe is constant
120s - Q5
The first law of thermodynamics states that energy can be neither created nor destroyed. For living organisms, which of the following is an important consequence of the first law?
Organisms are unable to transform energy.
The organism ultimately must obtain all of the necessary energy for life from its environment.
The entropy of an organism decreases with time as the organism grows in complexity.
Life does not obey the first law of thermodynamics.
the energy content of an organism is constant
120s - Q6
A chemical reaction that has a positive /\ G is correctly described as
endergonic
endothermic
enthalpic
exothermic
spontaneous
120s - Q7
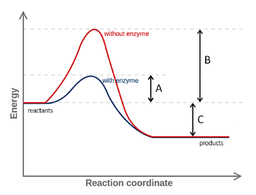
Which of the following statements regarding enzymes is true?
Enzymes decrease the free energy change of a reaction.
Enzymes are permanently altered by the reactions they catalyze.
Enzymes change the direction of chemical reactions.
Enzymes increase the rate of a reaction.
120s - Q8
The active site of an enzyme is the region that
is involved in the catalytic reaction of the enzyme.
binds the products of the catalytic reaction.
is inhibited by the presence of a coenzyme or a cofactor.
binds allosteric regulators of the enzyme.
120s - Q9
Increasing the substrate concentration in an enzymatic reaction could overcome which of the following?
saturation of the enzyme activity
competitive inhibition
denaturization of the enzyme
insufficient cofactors
allosteric inhibition
120s - Q10
What is a nonprotein "helper" of an enzyme molecule called?
allosteric group
enzyme activator
coenzyme
accessory enzyme
functional group
120s - Q11
Zinc, an essential trace element for most organisms, is present in the active site of the enzyme carboxypeptidase. The zinc most likely functions as a(n)
competitive inhibitor of the enzyme.
coenzyme derived from a vitamin.
cofactor necessary for enzyme activity.
allosteric activator of the enzyme.
noncompetitive inhibitor of the enzyme.
120s - Q12
Which of the following terms best describes the reaction?
allosteric
anabolic
endergonic
exergonic
120s - Q13
Which of the following bests describes the reaction?
negative /\ G, endergonic
positive /\ G, exergonic
negative /\ G, spontaneous
/\ G of zero, chemical equilibrium
positive /\ G, nonspontaneous
120s - Q14
How does a non-competitive inhibitor decrease the rate of an enzyme reaction?
by changing the free energy change of the reaction
by acting as a coenzyme for the reaction
by decreasing the activation energy of the reaction
by binding at the active site of the enzyme
by changing the structure of the enzyme
120s - Q15
What is the term for metabolic pathways that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules?
bioenergetic pathways
catabolic pathways
fermentation
anabolic pathways
thermodynamics
120s
