Practice
Quiz by Sara Wilking
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measure skillsfrom any curriculum
Measure skills
from any curriculum
Tag the questions with any skills you have. Your dashboard will track each student's mastery of each skill.
With a free account, teachers can
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
20 questions
Show answers
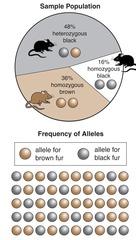
- Q1all the genes, including all alleles for each gene, that are present in a populationgene pool30s
- Q2number of times that an allele occurs in a gene pool as a percentage of the total occurrence of all alleles for that gene in that gene poolallele frequency30s
- Q3trait controlled by one gene that has two allelessingle-gene trait30s
- Q4trait controlled by two or more genespolygenic trait30s
- Q5form of natural selection in which individuals at one end of a distribution curve have higher fitness than individuals in the middle or at the other end of the curvedirectional selectional30s
- Q6form of natural selection in which individuals near the center of a distribution curve have higher fitness than individuals at either end of the curvestabilizing selection30s
- Q7natural selection in which individuals at the upper and lower ends of a distribution curve have higher fitness than individuals near the middle of the curvedisruptive selection30s
- Q8random change in allele frequency caused by a series of chance occurrences that cause an allele to become more or less common in a populationgenetic drift30s
- Q9a change in allele frequency following a dramatic reduction in the size of a populationbottleneck effect30s
- Q10change in allele frequencies as a result of the migration of a small subgroup of a populationfounder effect30s
- Q11situation in which allele frequencies in a population remain the samegenetic equilibrium30s
- Q12principle that states that allele frequencies in a population remain constant unless one or more factors cause those frequencies to changeHardy-Weinberg principle30s
- Q13when individuals select mates based on heritable traitssexual selection30s
- Q14the movement of genes into or out of a populationgene flow30s
- Q15a group of similar organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspringspecies30s