Q2_SUMMATIVE TEST #4
Quiz by Salvacion Adona
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measure skillsfrom any curriculum
Tag the questions with any skills you have. Your dashboard will track each student's mastery of each skill.
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
- Q1
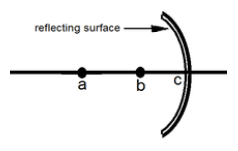
Which term refers to the length between b and c in the given figure?
Radius
Focal length
Center of curvature
Vertex
60s - Q2
Which of the following supports the laws of reflection?
I. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
II. The angle of incidence is greater than or less than the angle of reflection depending on
the medium.
III. The incident ray, the normal line, and the reflected ray lie on the same plane.
IV. The incident ray, the normal line and the reflected ray lie on different planes.
I & III
II & IV
I & IV
II & III
60s - Q3
Which is true about the image formed in the plane mirror?
I. Real
II. Virtual
III. Upright
IV. Inverted
V. Same size
VI. Magnified
VII. Diminished
I, IV, V
II, III, V
II, III, VII
I, IV, VII
60s - Q4
What image will be produced by a convex mirror?
Virtual, upright, larger than the object.
Real, inverted, larger than the object.
Real, inverted, smaller than the object.
Virtual, upright, smaller than the object.
60s - Q5
As shown in the figure below, a glass of water is placed in front of an arrow. Which of the following will most likely be the image you will perceive?
60s - Q6
If the light rays strike the diverging lens (as shown in the figure at the right), what will happen with the light rays?
Nothing will happen.
It will diverge at F’.
It will converge at F’.
It will bounce back on the same side.
60s - Q7
Where will the image form if the object is placed betweenF and 2F as shown in the figure on the right?
Beyond 2F’
At 2F’
At infinity
At F’
60s - Q8
What kind of image will be formed in this figure?
Real
No image will be formed
Virtual
Multiple images
60s - Q9
From the ray diagram of a double convex lens, why there is NO image formed when an object is located at the primary focus?
The incident ray pass through the optical center and refracted.
The incident light rays are intersected, and refracted rays are parallel.
The refracted rays are parallel lines and do not intersect at any point, so no image is formed along the lens’principal axis.
The two refracted rays are parallel to each other.
60s - Q10
A candle was placed 8 cm in front of a convex mirror having a focal length of
6 cm. Applying the ray diagramming, how do you described the image formed?
The image is inverted and diminished in size
The image is inverted, real and enlarged
The image is formed behind the mirror and enlarged
The image formed is virtual, upright, diminished in size, and located behind the mirror.
120s - Q11
Which is the correct orientation of the image produced by a Galilean telescope with respect to the object?
Upright
Real
Virtual
Inverted
60s - Q12
Why do astronomers prefer to use reflecting telescope in viewing astronomical objects?
It can preserve the colors of the object.
It produces an upright image of the object.
It collects less light than lenses.
It creates a clearer image of the object.
60s - Q13
A group of tourists wishes to see the “milky way”. Which optical instrument will give them a wider field of view?
Telescope
Compound microscope
Magnifying glass
Binoculars
60s - Q14
A compound microscope uses a system of lenses. Which property of light is observed in this device?
Dispersion
Reflection
Diffraction
Refraction
60s - Q15
Which instrument produces a virtual, larger, and upright image?
Astronomical telescope
Simple microscope
Camera
Compound microscope
60s