TEKS Biology High School - B.12.A: Biological Relationships
Quiz by TEKS Biology High School
High School - Biology
Science (2010) (Archived)
Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS)
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Track each student's skills and progress in your Mastery dashboards
With a free account, teachers can
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
12 questions
Show answers
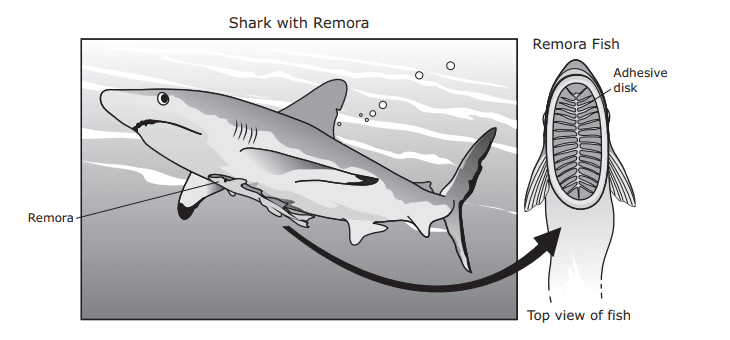
- Q1A remora is a fish that has an adhesive disk on the back of its head that it uses to attach itself to a large shark. When food floats away from the shark’s mouth as it feeds, the remora collects the scraps. Drawings of a shark with a remora attached and a remora’s adhesive disk are shown below. The relationship between the remora and the shark is an example of —competitioncommensalismpredationparasitism30sB.12.A: Biological Relationships
- Q2Four common relationships between organisms are listed in the box. Which statements best describe these relationships?Relationships 1, 2, and 4 are examples of mutualism. Relationship 3 is an example of parasitism.Relationship 1 is an example of commensalism. Relationships 2 and 4 are examples of mutualism. Relationship 3 is an example of predation.Relationships 1 and 2 are examples of commensalism. Relationships 3 and 4 are examples of mutualism.Relationships 1 and 4 are examples of mutualism. Relationship 2 is an example of commensalism. Relationship 3 is an example of parasitism.30sB.12.A: Biological Relationships
- Q3Some relationships between different organisms are shown in the table. Which table correctly identifies each type of interaction described?30sB.12.A: Biological Relationships
- Q4A student performed an investigation in which two ivy plants were planted in two separate containers. One of the containers had earthworms mixed in with the soil, and the other container had soil and no earthworms. The plants were given the same amount of water and exposed to the same amount of sunlight. The student observed that after several weeks of growth, the plant exposed to earthworms appeared to be healthier and exhibited more growth. To conclude that the relationship between the plant and the earthworm is an example of mutualism, the student must perform follow-up investigations that do which of the following?Determine whether the earthworms damage the soil in any wayDetermine whether the other plant in the investigation suffers as a result of not being exposed to earthwormsDetermine whether the earthworms benefit from being with the plantDetermine whether the water given to the plant is unpolluted30sB.12.A: Biological Relationships
- Q5Parrotfish are herbivores that are found in coral reefs. To escape predation, a parrotfish will graze with a rabbitfish, which has venomous spines at the end of its pelvic fins. The rabbitfish does not benefit from this relationship. Which type of relationship do the parrotfish and the rabbitfish have in the coral-reef environment?Parrotfish are herbivores that are found in coral reefs. To escape predation, a parrotfish will graze with a rabbitfish, which has venomous spines at the end of its pelvic fins. The rabbitfish does not benefit from this relationship. Which type of relationship do the parrotfish and the rabbitfish have in the coral-reef environment?MutualisticPredator–preyParasiticCommensal45sB.12.A: Biological Relationships
- Q6Bats eat insects that damage crops and mosquitoes that are vectors for disease. One million bats can eat several tons of insects per night, saving billions of dollars in pesticides yearly. Agricultural and public health scientists are concerned about the spread of white-nose syndrome (WNS). WNS is a result of a fungus that can infect cave-dwelling bats. While bats hibernate during winter months, the fungus covers the bats’ face and wings. WNS has a near 100% mortality rate, and 5.7 million bats have died since the discovery of the fungus in 2006. Many scientists are searching for ways to protect these bats. The relationship between this fungus and bats can best be defined as —commensal, because the bats provide a surface for the fungus to growcompetitive, because both organisms use caves as shelter during the winterparasitic, because the fungus obtains nutrients and shelter from the batsmutualistic, because the relationship involves two distinct species living together30sB.12.A: Biological Relationships
- Q7In any environment or ecosystem, organisms can have several different types of relationships. Three types of relationships are described below. Which of these correctly describes the relationships between the organisms?X: commensalism Y: parasitism Z: mutualismX: commensalism Y: mutualism Z: parasitismX: parasitism Y: commensalism Z: mutualismX: mutualism Y: parasitism Z: commensalism30sB.12.A: Biological Relationships
- Q8Brazil nuts (Bertholletia excelsa) are tall canopy trees that make up a large portion of the Amazon rain forest. They produce large grapefruit-sized seedpods. The agouti, a grounddwelling rodent, has teeth strong enough to open the tough seedpods. While the agouti eats some of the tree’s seeds, it also buries caches in various spots on the rain forest floor. Why is the agouti important to the rain forest ecosystem?It prevents the trees’ seeds from rotting on the rain forest floorIt cleans the rain forest floor of debris, allowing for easier motilityIt eats the trees’ excess seeds and prevents other animals from doing soIt eats and disperses the trees’ seeds30sB.12.A: Biological Relationships
- Q9The acacia ant (Pseudomyrmex ferruginea) lives in the bullshorn acacia plant, as shown below. The acacia ant nests and feeds in the plant’s hollow thorns. The ant helps protect the bullshorn acacia by attacking insects and grazing animals that come near the plant. The relationship between the acacia ant and the bullshorn acacia is an example of which of the following?MutualismNeutralismCommensalismParasitism30sB.12.A: Biological Relationships
- Q10A native species and a non-native species are competing for resources within the same ecosystem. The non-native species is more likely to survive than the native species in which of the following situations?The non-native species has no natural enemies in the ecosystemBoth the native species and the non-native species thrive on the same food sourceThe native species is immune to certain pathogens in the ecosystemPredators prey on both native and non-native species30sB.12.A: Biological Relationships
- Q11Which of these best demonstrates mutualism between certain types of bacteria and humans?Bacteria in improperly prepared food is consumed by humans, causing food poisoning.Bacteria become resistant to antibacterial medication that humans use for treatment.Intestinal bacteria obtain nutrients from the gut and produce vitamin K used by humans.Invasive bacteria at an area of injury produce toxins that damage healthy tissues of the human body.60sB.12.A: Biological Relationships
- Q12In North American forests, two species of birds, nuthatches and brown creepers, forage on the same trees for insects. Brown creepers feed on insects found near the bottom of the tree trunk, while nuthatches feed on insects in the top part of the tree. The difference in foraging behavior most likely affects the nuthatches and brown creepers by -allowing the birds to avoid many types of predatorspreventing the birds from interbreeding with each otherreducing competition between the birds for resourcesestablishing dominance between the birds for nesting sites60sB.12.A: Biological Relationships