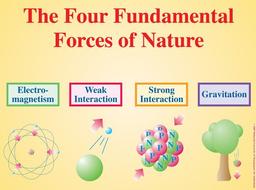
The 4 fundamental forces in the Universe
Quiz by Angie ♡
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measure skillsfrom any curriculum
Tag the questions with any skills you have. Your dashboard will track each student's mastery of each skill.
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
- Q1
Define gravitational force.
Gravity is the weakest force between all the fundamental forces.
all objects that have a mass which attract each other with a force, meaning the force of attraction between all masses in this universe.
Gravity is everything that goes down has to go up.
Gravity is earth.
30s - Q2
What does gravity do .
The pull between the sun, the planets and the earth.
The pull between atomic nuclei.
The pull between any objects with mass.
The pull between Earth and the moon.
15s - Q3
List the four fundamental forces of nature in order from weakest to strongest
Electromagnetism, Gravity, Strong Nuclear force, Weak Nuclear force.
Weak Nuclear force, Gravity, Electromagnetism, Strong Nuclear force.
Weak Nuclear force, Electromagnetism, Gravity, Strong Nuclear force.
Gravity, Weak Nuclear force, Electromagnetism, Strong Nuclear force.
30s - Q4
Gravity has a range that is ____________.
Long.
short.
medium.
Infinity.
15s - Q5
When an atom undergoes radioactive decay, it is due to.
Weak nuclar force.
Electromagnetism.
strong nuclear force.
Gravity.
15s - Q6
Define weak force.
The weak force is one of the four fundamental forces that does not govern all matter in the universe.
reaction between the particles that causes the radioactive substances to break down into different pieces.
Weak force is the stongest out of all the forces.
Weak force is a force that is weak.
15s - Q7
____________ and ____________ are short range forces.
Gravity, Electromagnetism.
Gravity, Weak Nuclear.
Strong Nuclear, Weak Nuclear.
Electromagnetism, Strong Nuclear.
15s - Q8
An electron moving in wire is an example of
Electromagnetism
Strong Nuclear
Gravity
Elect
15s - Q9
What causes electromacnetic waves ?
Anything that has electricity.
waves with energy.
power.
an electrical current flows through a simple conduct
15s - Q10
Define electromagnetism?
A force that just gives electricity.
A force that is the weakest.
A force that is just particles in earth.
A branch of Physics that deals with the electromagnetic forces that occur between charged particles, these particles come from electricity this is a way they get charged.
15s - Q11
_____________ is the force that binds protons together in the nucleus of an atom.
Stong nucleus force.
Gravitational force.
Weak nuclear force
Electomagnetisim
15s - Q12
the strong force is not the strongest force betwen all the fundamental forces.
falsetrueTrue or False15s - Q13
Define strong force
A force that is strong.
The strong forcethat does not hold the quarks together.
A force that has a lot of power and its heavy.
a fundamental interaction of nature that acts between subatomic particles of matter.
15s - Q14
When an atom undergoes radioactive decay, it is due to:
Electromagnetism.
None of the above.
Weak Nuclear.
Gravity.
15s - Q15
This is the right order from strongest to weakest > 1) the strong nuclear force, 2) the electromagnetic force, 3) the weak nuclear force, and 4) gravity.
truefalseTrue or False20s