The Economic Problem: Scarcity
Quiz by Sharon Barry
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measure skillsfrom any curriculum
Tag the questions with any skills you have. Your dashboard will track each student's mastery of each skill.
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
- Q1
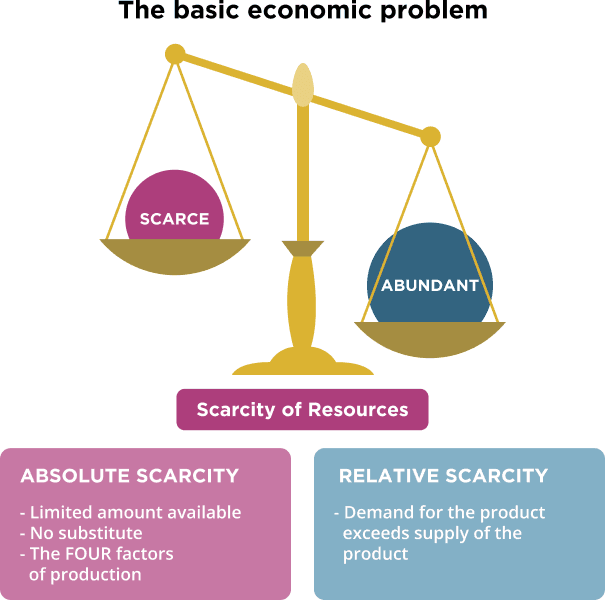
Relative scarcity exists...
where the demand for a good is greater than the supply of a good.
when there is no good or service available, and one does not have the resources to acquire it.
when poverty rates increase.
when the government invests in education and training to address skills shortages in the country.
30s - Q2
Absolute scarcity is when
there is a shortage of land and limited means to access more
there is a shortage of entrepreneurial skills and limited means to develop them
no resources available to satisfy the existing needs and wants, and no substitute products
there is a shortage of money and limited means to access more
30s - Q3
Scarce factors of production include
land; entrepreneurship; labour; capital
machines; skills; money; time
imports; exports; public services; interest
land; products; services; money
30s - Q4
The more our wants and needs are satisfied, the more we want is an example of:
relative scarcity
people having enough money to buy whatever they want
supply overtaking demand
absolute scarcity
30s - Q5
The following statement is true about poverty and scarcity:
poverty and relative scarcity are similar
poverty is another word for scarcity
only poor people experience scarcity
Resources are so scarce that not even basic needs can be met
30s - Q6
Tshepo wants to go to movies and hang out at the arcade with his friends. A movie ticket is R56 and the different games at the arcade cost R10 each. His mom gives him R60. The following statement is true about Tshepo:
He has to make a choice because he has limited resources
He is faced with the economic problem of absolute scarcity
Poverty forces him to have to choose
He can go to movies and play 3 games
30s - Q7
Tshepo wants to go to movies and hang out at the arcade with his friends. A movie ticket is R56 and the different games at the arcade cost R10 each. His mom gives him R60. He chooses to go to the movies. The following statement is true about Tshepo:
Only the poor are faced with opportunity costs
Going to the movies is the opportunity cost of his choice
His choice is prompted by absolute scarcity
Going to the arcade with his friends is the opportunity cost of his choice
30s - Q8
The following are all examples of economic goods, except:
"MrP" Hoodie
A new Kia
Clean water
Nike sneakers
30s - Q9
You have R50. You want to buy a burger and fries with a milkshake for R30 and a ticket to the IMAX action movie for R40. Is this an example of where you will incur an opportunity cost?
No, because it would be possible to buy the meal and see the movie.
Yes, there will be an opportunity cost because you do not have enough money for both activities.
No, because you will choose the cheaper option which means there is no opportunity cost.
The opportunity cost can be avoided by choosing neither option and rather keeping your money.
30s - Q10
Which one of these definitions best describe Opportunity costs?
the cost of spending more than you have
The cost for the opportunity to buy anything you want.
the cost of what you didn't choose when making one decision over another
The cost of buying something expensive
30s - Q11
Selling hand made jewelry at a Flea market is an example of
Primary production
Secondary production
opportunity costs
Tertiary production
30s - Q12
Refining crude oil is an example of:
primary production
sustainable environmental processing
secondary production
tertiary production
30s - Q13
The following is an example of a semi-durable good:
A new washing machine
A Nike hoodie
A Big Mac and Fries
Being served coffee at a coffee shop
30s - Q14
The following activities all happen in a marketplace, except:
Exchange for goods and services
Negotiations about quantities and price
Communication between producers and consumers
Final products are produced
30s - Q15
The government builds a new road to replace an old inadequate road. This is an example od
Government individual consumption expenditure
Government collective consumption expenditure
Regional primary production practices
Foreign market expenditure
30s