Topic 3 Review
Quiz by Fred Spies
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measure skillsfrom any curriculum
Tag the questions with any skills you have. Your dashboard will track each student's mastery of each skill.
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
- Q1
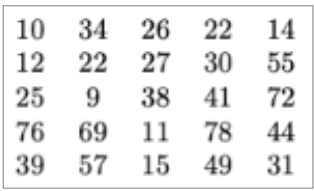
Which of the following is the number of classes needed to divide the data into equal classes of 10-point intervals?
10 classes
8 classes
7.7 classes
7 classes
12 classes
120s - Q2
If a student obtained a score of 25 or less, they have to retake the test. How many students have to retake the test.
8 students
10 students
9 students
120s - Q3
Which of the following is the least complex level of data measurement?
Nominal
Interval
Ratio
Ordinal
120s - Q4
Different species of predatory birds are arranged from largest population to smallest population. In terms of data collection, this is an example of…
Ordinal measurement
Interval measurement
Ratio measurement
Nominal measurement
120s - Q5
Which of the following is an example of ordinal data?
A person’s hair color
Breeds of dogs
Performance rankings
120s - Q6
Which of the following is an example of ratio-level data?
Measurement of age
Satisfaction levels of patients in a hospital
Blood types of patients in a hospital
120s - Q7
How many students weigh between 30 - 40 kg?
5 students
11 students
120s - Q8
How many students weigh between 20 - 50 kg?
18 students
16 students
11 students
120s - Q9
Is the data in the following table organized as exclusive or inclusive intervals?
Inclusive
Exclusive
120s - Q10
What is the highest level of measurement in the following table? (Select the most correct answer)
Interval
Ratio
Ordinal
All of the above
120s - Q11
The following scores can be considered ratio measurement. If we changed the grading to letters “A, B, C, D, etc”, would that change the level of measurement?
No
Yes
Not enough data
120s - Q12
Convert the following into a cumulative frequency table. Less than 39 is…
3
43
4
120s - Q13
Convert the following into a cumulative frequency table. Less than 99 is…
3
43
4
120s - Q14
Convert the following into a cumulative frequency table. More than 69 is…
12
11
43
120s - Q15
Explain why the temperature outside in degrees Kelvin is a ratio measurement and in degrees Celsius is an interval measurement.
The Celsius scale 0, is not the end of the scale, because it can go negative. The Kelvin scale 0, is absolute zero and cannot go lower.
The Kelvin scale 0, is not the end of the scale, because it can go negative. The Celsius scale 0, is absolute zero and cannot go lower.
120s