Topic: 6.8-6.9 Force, Motion and Energy
Quiz by Grade 6 Science - Texas Education Agency
Grade 6
Science (2017)
Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS)
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measures 4 skills from
Measures 4 skills from
With a free account, teachers can
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
20 questions
Show answers
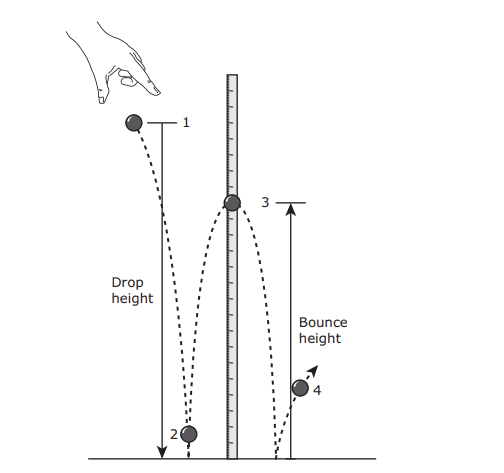
- Q1In the classroom demonstration shown below, a rubber ball is dropped from Position 1. The ball bounces as shown. At which of these positions does the ball have both the greatest kinetic energy and the least potential energy?Position 1Position 2Position 4Position 360s6.8a
- Q2A car travels at a constant speed of 15 m/s for 2 minutes. The car increases its speed from 15 to 25 m/s during the next minute and then travels at a constant speed of 25 m/s for 2 more minutes. Which of the following graphs best represents the car’s motion during this 5-minute period?#texas/83c26e54-1342-4a8c-a460-b3bc9f4ea49f/C.png#texas/83c26e54-1342-4a8c-a460-b3bc9f4ea49f/B.png#texas/83c26e54-1342-4a8c-a460-b3bc9f4ea49f/D.png#texas/83c26e54-1342-4a8c-a460-b3bc9f4ea49f/A.png60s6.8d
- Q3A student walks 2 km in 30 minutes. What is the student’s average speed in km/h? Be sure to use the correct place value.Users enter free textType an Answer60s6.8c
- Q4The diagram below shows a hot air balloon rising. Propane gas tanks are seen at the bottom of the balloon. What energy transformations occur when propane gas is used to lift the balloon?Thermal → chemical → lightChemical → thermal → mechanicalChemical →mechanical → thermalMechanical → light→ chemical60s6.9c
- Q5The main parts of a working clothes dryer are shown in the diagram. This appliance dries clothes primarily by converting —mechanical energy to heat and electrical energymechanical energy to heat and vaporizationelectrical energy to heat and mechanical energyelectrical energy to heat and light60s6.9c
- Q6A bus travels 20 km in 30 minutes. What is the average speed of the bus?30 km/h40 km/h20 km/h50 km/h60s6.8c
- Q7A student drew the diagram below to show the movement of water through a hydroelectric dam. The student used the diagram to describe changes in the potential and kinetic energy of the water. At which location is the gravitational potential energy of the water the greatest?Location XLocation YLocation WLocation Z60s6.8a
- Q8A student runs two times around a running path at a local park. Each lap is 3 km. The student completes the first lap in 20 minutes. The student then sits on a bench and rests for 5 minutes before completing the second lap in 25 minutes. Which graph best represents the student’s motion?#texas/3b333deb-3d2d-4f0a-bead-bafc9856e79e/A.png#texas/3b333deb-3d2d-4f0a-bead-bafc9856e79e/C.png#texas/3b333deb-3d2d-4f0a-bead-bafc9856e79e/D.png#texas/3b333deb-3d2d-4f0a-bead-bafc9856e79e/B.png60s6.8d
- Q9A cook heats a meal in a microwave oven. What energy transformations occur between the microwave oven and the meal?Chemical energy → thermal energy → light energyElectrical energy → electromagnetic energy → thermal energyChemical energy → electromagnetic energy → chemical energyElectrical energy → light energy → chemical energy60s6.9c
- Q10A bicycle rider is traveling up a hill. When the rider reaches the top of the hill, she stops to rest. Then she travels down the hill. The diagram shows the rider in the three different positions. Which of these correctly describes the potential energy and the kinetic energy of the bicycle rider?As the rider reaches the bottom of the hill, her kinetic energy and her potential energy decrease.When the rider is at the top of the hill, her potential energy is the greatest, and her kinetic energy is the least.When the rider goes down the hill, her potential energy increases, and her kinetic energy decreases.As the rider moves up the hill, her kinetic energy increases, and her potential energy decreases.60s6.8a
- Q11A golfer collected data on the distance a golf cart traveled in a straight line and plotted it on a graph. Which of these does NOT describe the cart’s motion on this graph?The cart moved 11 m toward the starting point between 8 s and 10 s.The cart moved away from the starting point at a speed of 1 m/s for 2 s.The cart moved 24 m away from the starting point between 2 s and 5 s.The cart moved toward the starting point at a speed of 3 m/s between 7 s and 12 s.60s6.8d
- Q12A student kicks a soccer ball three times. Another student records the distance, the amount of time the ball travels, and the average speed in the table shown below. How many seconds did it take for the ball to travel 30 m during Kick 3?1.5 s2.0 s1.0 s0.5 s60s6.8c
- Q13Four students were asked to classify the activities of the people in the picture below as examples of either potential or kinetic energy. Which student correctly classified the activities?#texas/97806e28-19b5-4a15-9f31-eb49e51af5a5/A.png#texas/97806e28-19b5-4a15-9f31-eb49e51af5a5/C.png#texas/97806e28-19b5-4a15-9f31-eb49e51af5a5/D.png#texas/97806e28-19b5-4a15-9f31-eb49e51af5a5/B.png60s6.8a
- Q14When a lion eats a zebra and then uses the energy from the zebra to run, the lion’s body converts —chemical energy to mechanical energychemical energy to light energymechanical energy to chemical energyelectrical energy to chemical energy60s6.9c
- Q15The graph below shows distance over time. Which of these situations could be represented by this graph?A student walks 1.5 km to a friend’s house in 20 minutes. The two students then walk another 1.5 km to school in 60 minutes.A student walks 1.5 km to a friend’s house in 20 minutes. The two students then walk another 1.5 km to school in 40 minutes.A student walks 1.5 km to a friend’s house in 30 minutes. The two students then walk another 1.5 km to school in 30 minutes.A student walks 1.5 km to a friend’s house in 40 minutes. The two students then walk another 1.5 km to school in 20 minutes.60s6.8d