Unit 1: Atoms and the Periodic Table
Quiz by Janice Bixler
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measures 3 skills from
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
- Q1
Compare and contrast protons and neutrons. Place the label under each correct category. Some categories may contain more than one answer.
Users sort answers between categoriesSorting60sSPS1a - Q2
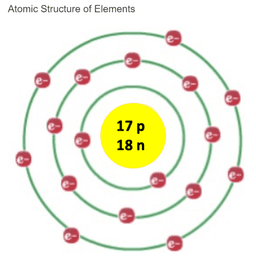
Chlorine is the atomic number 17 in the periodic table of elements. What information does the atomic number give you about the element chlorine?
An atom of chlorine has 17 protons+ and 17 neutrons+.
An atom of chlorine has 17 protons+.
An atom of chlorine has 17 protons+ and neutrons- combined.
Chlorine atoms have 17 of each of three subatomic particles, protons, neutrons, and electrons.
30sSPS1a - Q3
Chlorine is the atomic number 17 in the periodic table of elements. Based on that knowledge, which of these statements is NOT true concerning the atomic structure of aluminum?
Aluminum has an atomic number of 13.
Aluminum has 13 protons+ in the nucleus.
Aluminum has 13 neutrons.
The number of protons equals the number of electrons.
30sSPS1a - Q4
Using the periodic table and your knowledge of atomic structure. Draw a conclusion about the number of neutrons in Carbon-14 relative to a typical carbon atom.
It has less neutrons. Its mass number is smaller than the one on the periodic table.
The periodic table cannot give you the information needed to answer this question.
It has more neutrons. Its mass number is larger than the atomic mass number for carbon.
The same number of neutrons. All carbon atoms have atomic number 6.
30sSPS1a - Q5
How would the composition of an atom change if both the atomic number and mass number each increase by one?
The atom would have one more proton and one more neutron.
The atom would have one more proton, one more neutron and one more electron.
The atom would have 1 more neutron.
The atom would have one more proton and electron.
30sSPS1a - Q6
How many electrons are in Potassium?
19
39
20
21
30sSPS1a - Q7
What is the number of neutrons in boron?
5
6
10
11
30sSPS1a - Q8
How many electrons are in helium?
4
2
5
3
30sSPS1a - Q9
The atomic masses of the elements are not whole value numbers because of the existence of
isotopes.
ions.
protons.
quarks.
30sSPS1a - Q10
The sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons in an atom is the
number of isotopes.
mass number.
valence electrons.
atomic number.
30sSPS1a - Q11
Hydrogen is different than the other elements in group 1 of the periodic table by
being a gaseous material.
freezing easily.
being highly reactive.
only having one electron in outer energy level.
30sSPS1c - Q12
The weighted average of the mass numbers of all the isotopes that occur in nature for a particular element is the
atomic number.
number of neutrons.
atomic mass.
number of electrons.
30sSPS1a - Q13
The isotopes of carbon are carbon-12 and carbon-14. These isotopes differ from one another by
two protons.
two atoms.
two electrons.
two neutrons.
30sSPS1a - Q14
Why are the elements in group 18 stable?
The atoms in group 18 are considered to be isotopes.
The atoms in group 18 have 18 neutrons in the nucleus to make them stable.
The atoms in group 18 have outer energy levels contain 8 electrons, except helium.
The atoms in group 18 have 18 energy levels which makes them stable.
30sSPS1c - Q15
The chart showing the classification of elements according to their properties and increasing atomic numbers is called the
Mendeleev chart.
periodic table.
chemistry.
periodic desk.
30sSPS1b