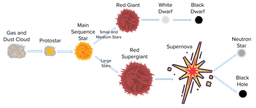
UNIT 2 TEST - LIFE CYCLE OF STARS
Quiz by Daryl Cadanilla
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measure skillsfrom any curriculum
Tag the questions with any skills you have. Your dashboard will track each student's mastery of each skill.
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
- Q1
Where are stars created or "born"?
dwarf galaxy
nebula
black hole
main sequence
30s - Q2
What stage of a star's life is the protostar?
the second stage, where gravity is the main source of energy
the first stage of gases and dust
the final stage
the fourth stage, where helium is fusing into larger elements
30s - Q3
What factor contributes to the stability of stars during the main sequence stage, preventing them from collapsing despite gravitational pull?
The balance between gravitational forces and nuclear fusion energy
The presence of a solid outer layer
A constant influx of new material from surrounding space
The release of gravitational energy as heat
30s - Q4
Which is true about main sequence stars?
All stars in the main sequence category are very luminous
Main sequence stars are large.
They fuse hydrogen into helium.
30s - Q5
Which color of stars are the hottest?
yellow
red
blue
white
30s - Q6
Identify the inner most layer of the sun.
core
chromosphere
corona
photosphere
30s - Q7
A black hole is an object so dense and with so much gravity that even ___ cannot escape.
men
light
spaceship
alien
30s - Q8
Which type of stars will become supergiants?
massive
small - average sized stars
30s - Q9
What is the name of the largest stars?
supergiants
giants
neutron star
supernova
30s - Q10
What is the name of the explosion at the death of a supergiant?
supernova
black hole
nebula
black dwarf
30s - Q11
This red star has about the same temperature as Mira but is much dimmer. Which type of star is this?
main sequence
giant
white dwarf
supergiant
30s - Q12
The H-R diagram is a graph that show the relationship between _________ for stars?
temperature and brightness
temperature and distance
temperature and pressure
brightness and color
30s - Q13
When does a star become a red giant?
During the main sequence phase
After it forms from a protostar
After it goes supernova
After it exhausts hydrogen in its core and begins to fuse helium
30s - Q14
Which of the following statements best explains the relationship between a star's mass and its life cycle stages, including its ultimate fate?
High-mass stars burn hydrogen faster than low-mass stars, resulting in longer lifespans for high-mass stars.
All stars follow the same evolution path, regardless of their mass, eventually becoming red giants and white dwarfs.
Stars with the same initial mass will always produce the same types of nucleosynthesis products, regardless of their subsequent evolution.
Low-mass stars evolve into red giants and end their lives as white dwarfs, while high-mass stars undergo supernova explosions and become neutron stars or black holes.
30s - Q15
Based on the Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram, which area represents stars that are cool and bright?
top right
top left
bottom left
bottom right
30s