Unit 5 - Mountains and Climate
Quiz by 7science PMS
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measure skillsfrom any curriculum
Tag the questions with any skills you have. Your dashboard will track each student's mastery of each skill.
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
- Q1
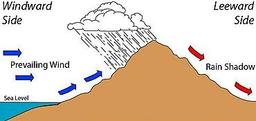
Compare the windward and leeward side of a mountain. Describe the air on the windward side of a mountain.
Users link answersLinking60s - Q2
Describe the air on the leeward side of a mountain.
moist & warm
moist & cool
dry & warm
dry & cool
30s - Q3
The vegetation on the windward side could be
prairies
thick forests
deserts
grasslands
60s - Q4
The vegetation on the leeward side could be
thick forests
tall trees
drought resistant plants
lots of grass
60s - Q5
As air moves down the leeward side of a mountain it gets
thicker
warmer
moister
colder
60s - Q6
Which side of the mountain usually gets deserts and why?
leeward, because of rising, dry air
leeward, because of sinking, dry air
windward, because of rising, moist air
windward, because of sinking, moist air
60s - Q7
As air rises, it expands. This expanding air will then do what when it's at a high enough altitude?
warms and condenses
cools and condenses
30s - Q8
Which description best matches desert biome ?
Dry environments that generally receive less than 10 in. of rainfall each year.
A cold, dry, mostly treeless biome that encircles the Arctic Ocean
Near the equator, warm temperatures, and abundant rainfall.
60s - Q9
Which of these is NOT a type of desert?
coastal
polar
interior
rain shadow (hot)
tropical
subtropical (warm)
30s - Q10
What is the rainshadow effect?
The Rain Shadow Effect is a phenomenon where a region experiences equal rainfall on both sides of a mountain range.
The Rain Shadow Effect is a phenomenon where a region experiences rainfall only on the windward side of a mountain range.
The Rain Shadow Effect is a phenomenon where a region experiences significantly more rainfall on the leeward side of a mountain range.
The Rain Shadow Effect is a phenomenon where a region experiences significantly less rainfall on the windward side of a mountain range.
120s - Q11
What is the leeward side of a mountain?
The leeward side of a mountain is the side that faces the prevailing winds.
The leeward side of a mountain is the side that is located at the top of the mountain.
The leeward side of a mountain is the side that is sheltered from the prevailing winds.
The leeward side of a mountain is the side that is exposed to the prevailing winds.
120s - Q12
Which physical feature is a main cause of the rain shadow effect?
Mountains near large bodies of water
Deserts on the inside of a continent
Valleys near large bodies of water
Volcanoes near plate boundaries
60s - Q13
What happens to the air as it rises over the mountains in the rainshadow effect?
The air cools and drops water vapor as precipitation.
The air becomes drier and loses moisture.
The air flows faster and creates strong winds.
The air becomes warmer and more humid.
120s - Q14
Which side of the mountains in Washington receives more precipitation?
Northern side
Western side
Eastern side
Southern side
60s - Q15
How does being on the leeward side of the mountains impact the vegetation in Washington?
Abundant vegetation
No impact on vegetation
Limited vegetation
Increased vegetation
60s