Week 5 Quiz
Quiz by Joseph Cicchillo
Feel free to use or edit a copy
includes Teacher and Student dashboards
Measure skillsfrom any curriculum
Measure skills
from any curriculum
Tag the questions with any skills you have. Your dashboard will track each student's mastery of each skill.
With a free account, teachers can
- edit the questions
- save a copy for later
- start a class game
- automatically assign follow-up activities based on students’ scores
- assign as homework
- share a link with colleagues
- print as a bubble sheet
7 questions
Show answers
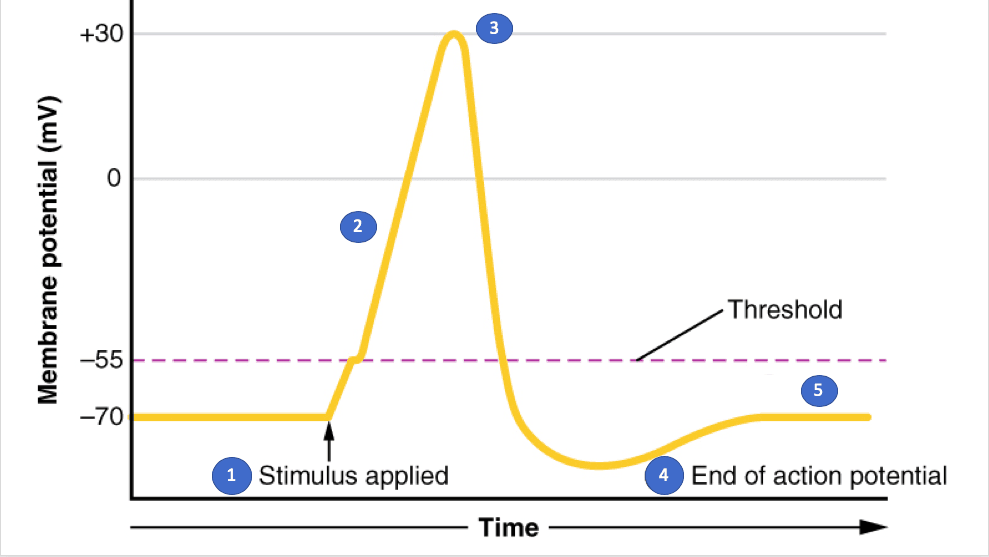
- Q11.K+ diffuses out of cellStimulus Hyperpolarizes membraneNa+ diffuses out of cellStimulus is applied that brings membrane to threshold30s
- Q22.Voltage-gated K+ channels openK+ rushes into cell causing hyperpolarizationLeaky Na+ channels open causing depolarizationVoltage-gated Na+ channels open causing depolarization30s
- Q33.Voltage-gated K+ channels close and voltage-gated Na+ channels open causing HyperpolarizationNa+ rushes into cell causing HyperpolariationVoltage-gated Na+ channels close and voltage-gated K+ channels open causing RepolarizationK+ rushing into cell causing Depolarization30s
- Q44.Leaky K+ channels closeNa+/K+ pump closesVoltage-gated K+ channels close, but are sluggish causing HyperpolarizationLeaky Na+ channels become inactive30s
- Q55.Leak channels closeVoltage gated Na+ opens to depolarize the cell and bring it to its resting potentialMembrane potential returns to normal via Na+/K+ pumpLeak channels open via ATP to restore membrane potential30s
- Q6What does the Absolute Refractory Period tell us about the neuron?The neuron is ready to send another signalThe nerve can only be stimulated if the signal is strong enoughPeriod of time when a nerve can not be stimulated because it is already sending a signal30s
- Q7What does the Relative Refractory Period tell us about the neuron?Only an exceptionally strong stimulus can generate an Action PotentialThe neuron cannot be stimulated under any circumstance30s